Autoimmune Disease
Introduction
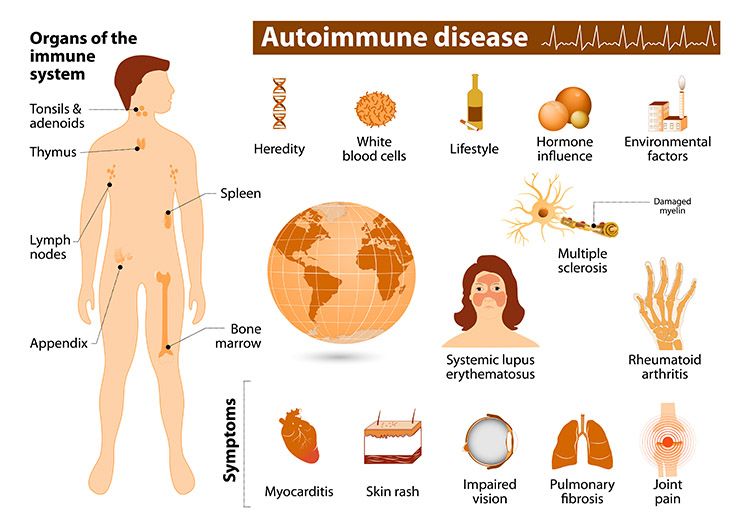
Autoimmune diseases represent a complex group of disorders characterized by the immune system attacking the body's own healthy tissues. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the various aspects of autoimmune diseases, including their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and recent research findings. Additionally, we will provide resources for further information and support.
What is autoimmune disease?
An autoimmune disease occurs when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy tissues, mistaking them for harmful invaders. This immune response can lead to inflammation and damage to various organs and systems within the body. There are over 80 different autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, type 1 diabetes, and multiple sclerosis.
Who's at risk for autoimmune disease?
While anyone can develop an autoimmune disease, certain factors can increase the risk. These include:
- Genetics: Individuals with a family history of autoimmune diseases have a higher risk of developing one themselves.
- Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop autoimmune diseases, particularly during their childbearing years.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain infections, chemicals, or pollutants may trigger the development of an autoimmune disease.
- Ethnicity: Some autoimmune diseases are more prevalent in certain ethnic groups.
What causes autoimmune disease?
The exact cause of autoimmune diseases remains unknown. However, researchers believe that a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors contribute to their development. Some proposed triggers include infections, drug reactions, exposure to chemicals, and physical or emotional stress.
How does autoimmune disease start?
Autoimmune diseases begin when the immune system loses its ability to differentiate between foreign substances and the body's own healthy cells. This leads to an immune response against the body's tissues, causing inflammation and damage.
What are the symptoms of autoimmune disease?
Symptoms of autoimmune diseases vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. However, some common symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Joint pain and swelling
- Skin rashes
- Digestive problems
- Fever
- Weight loss or gain
- How is autoimmune disease diagnosed?
Diagnosing an autoimmune disease can be challenging, as the symptoms often mimic those of other illnesses. A healthcare provider will typically start with a thorough medical history and physical examination. Blood tests, imaging studies, and biopsies may be used to help confirm a diagnosis and rule out other potential causes.
How can autoimmune disease be treated?
While there is no cure for autoimmune diseases, treatment aims to manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent further damage to the body. Depending on the specific condition, treatment options may include:
- Medications, such as anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressive agents
- Physical therapy to improve mobility and reduce pain
- Dietary changes to reduce inflammation and promote overall health
- Stress management and mental health support
What complications may occur with autoimmune disease?
Untreated or poorly managed autoimmune diseases can lead to a variety of complications, such as:
- Organ damage
- Increased risk of infections
- Development of additional autoimmune diseases
- Mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety
How can I prevent autoimmune disease?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent autoimmune diseases, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk.
This includes:
- Eating a well-balanced diet
- Exercising regularly
- Getting enough sleep
- Reducing stress
- Avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals and pollutants
Long-term management of Back Pain
Some autoimmune diseases can cause chronic back pain. Long-term management strategies may include:
- Medications for pain relief and inflammation reduction
- Physical therapy and exercise to maintain strength and flexibility
- Ergonomic modifications at work or home to minimize strain on the back
- Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, and chiropractic care
- Mental health support to cope with the emotional impact of chronic pain
What is recent research saying about autoimmune disease?
Recent research on autoimmune diseases has focused on understanding the underlying causes, improving diagnosis and treatment, and identifying potential preventative measures. Some key findings include:
- The role of the gut microbiome in modulating the immune system and its potential impact on autoimmune diseases
- The use of precision medicine to tailor treatments for specific patients based on their genetic makeup
- The potential for stem cell therapy in repairing damage caused by autoimmune diseases
- The development of new medications that target specific immune pathways to minimize side effects and improve treatment efficacy
Where can I go for more information on autoimmune disease?
For more information and support, consider the following resources:
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS): www.niams.nih.gov
- Autoimmune Association: www.autoimmune.org
- Autoimmune Diseases Support Community (Inspire): www.inspire.com/groups/autoimmune-diseases
Autoimmune diseases are complex and often challenging to diagnose and treat. However, understanding their causes, symptoms, and management options can help individuals and healthcare providers work together to improve patient outcomes. As research continues to expand our knowledge, the future holds promise for new treatments and preventative strategies to help those affected by autoimmune diseases live healthier, more fulfilling lives.

