Esophageal Cancer
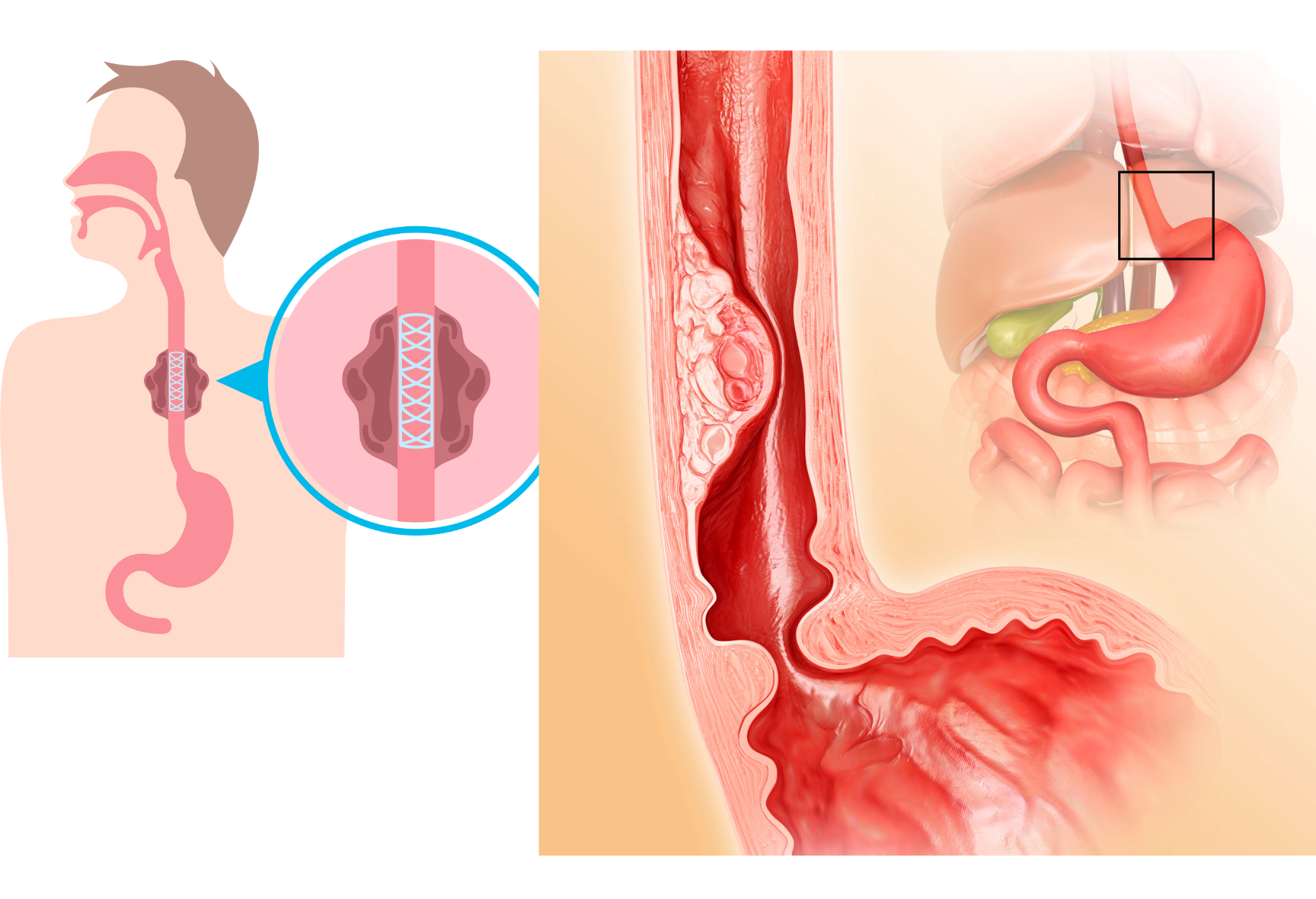
Esophageal cancer is a malignant tumor that develops in the lining of the esophagus, the tube connecting the mouth to the stomach. In this article, we will address common questions about esophageal cancer, including its causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and long-term management.
What is esophageal cancer?
Esophageal cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the cells lining the esophagus. There are two main types of esophageal cancer: squamous cell carcinoma, which develops in the flat, thin cells that line the esophagus, and adenocarcinoma, which starts in the glandular cells located at the lower part of the esophagus.
Who’s at risk for esophageal cancer?
Several factors can increase the risk of developing esophageal cancer, including:
- Age: Esophageal cancer is more common in people aged 55 and older.
- Gender: Men are more likely to develop esophageal cancer than women.
- Tobacco and alcohol use: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption increase the risk of esophageal cancer.
- Obesity: Excess body weight can contribute to the development of adenocarcinoma.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): Chronic acid reflux may increase the risk of esophageal cancer.
- Barrett's esophagus: A condition in which the cells lining the lower esophagus are replaced by abnormal cells, increasing the risk of adenocarcinoma.
- Diet: A diet low in fruits and vegetables may be associated with an increased risk of esophageal cancer.
What causes esophageal cancer?
The exact cause of esophageal cancer is not well understood. However, it is believed that damage to the cells lining the esophagus due to factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and chronic acid reflux can lead to the development of cancerous cells.
How does esophageal cancer start?
Esophageal cancer begins when cells in the lining of the esophagus develop mutations in their DNA, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and the formation of a tumor. Over time, the tumor can grow and potentially spread to other parts of the body.
What are the symptoms of esophageal cancer?
Common symptoms of esophageal cancer include:
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Indigestion or heartburn
- Coughing or hoarseness
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other, less serious conditions. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation.
How is esophageal cancer diagnosed?
To diagnose esophageal cancer, a healthcare professional may perform several tests, including:
- Physical examination: A thorough examination to check for any abnormalities.
- Endoscopy: A thin, flexible tube with a light and camera (endoscope) is passed down the throat to examine the esophagus and look for signs of cancer.
- Biopsy: During an endoscopy, a small sample of tissue may be taken for further examination under a microscope.
- Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans, or PET scans may be used to determine the extent of the cancer and whether it has spread to other parts of the body.
How can esophageal cancer be treated?
Treatment for esophageal cancer depends on the type, stage, and location of the cancer, as well as the patient's overall health. Treatment options may include:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor and surrounding tissue, which may involve partial or complete removal of the esophagus.
- Chemotherapy: The use of drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy: The use of high-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy: The use of drugs that target specific proteins or other molecules involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells.
In some cases, a combination of these treatments may be used to achieve the best possible outcome.
What complications may occur with esophageal cancer?
Esophageal cancer can lead to several complications, including:
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Malnutrition and weight loss
- Bleeding in the esophagus
- Obstruction of the esophagus
- Spread of cancer to other parts of the body (metastasis)
How can I prevent esophageal cancer?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent esophageal cancer, some steps may help reduce the risk of developing the disease, including:
- Quit smoking and avoid excessive alcohol consumption
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Eat a diet rich in fruits and vegetables
- Manage acid reflux and treat Barrett's esophagus
- Seek regular medical care and screenings
Long-term management of esophageal cancer
After treatment for esophageal cancer, long-term management may involve regular follow-up care to monitor for any signs of recurrence or complications. Patients may also need to make certain lifestyle changes, such as modifying their diet or engaging in regular physical activity, to support their overall health and recovery.
What is recent research saying about esophageal cancer?
Recent research on esophageal cancer has focused on identifying new treatment options, improving diagnosis and staging methods, and exploring the potential role of genetics and immune system function in the development and progression of the disease.
Where can I go for more information on esophageal cancer?
For more information on esophageal cancer, consult your healthcare provider or a qualified medical professional, such as an oncologist or gastroenterologist. Reputable online resources, such as the American Cancer Society or the National Cancer Institute, can also provide valuable information and support for those affected by esophageal cancer.

