Meningitis
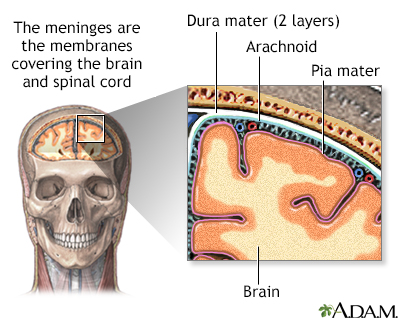
What is meningitis?
Meningitis is a serious condition characterized by inflammation of the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
Who's at risk for meningitis?
Anyone can develop meningitis, but certain individuals are at higher risk, including:
- Infants and young children
- Adolescents and young adults
- Individuals with weakened immune systems
- Individuals living in crowded or communal settings, such as college dormitories or military barracks
- Individuals who have had close contact with someone with meningitis
What causes meningitis?
Meningitis can be caused by a variety of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. In some cases, the cause of meningitis may be unknown.
How does meningitis start?
Meningitis typically begins with symptoms such as fever, headache, and neck stiffness. These symptoms can develop rapidly over a few hours or may take several days to appear.
What are the symptoms of meningitis?
Symptoms of meningitis may include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Neck stiffness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sensitivity to light
- Confusion or altered mental status
- Rash (in some cases)
How is meningitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of meningitis typically involves a physical exam, blood tests, and imaging tests such as a CT scan or MRI. A sample of cerebrospinal fluid may also be taken through a lumbar puncture to help diagnose the condition.
How can meningitis be treated?
Treatment for meningitis depends on the cause of the infection and may include antibiotics, antiviral medications, or antifungal medications. Supportive care such as IV fluids and pain management may also be necessary.
What complications may occur with meningitis?
Complications of meningitis may include:
- Brain damage
- Hearing loss
- Vision loss
- Seizures
- Coma
- Death
How can I prevent meningitis?
Prevention of meningitis includes:
Vaccination: Vaccines are available for certain types of meningitis, including meningococcal, pneumococcal, and Hib meningitis.
Avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick: Meningitis can be spread through close contact with an infected individual, so avoiding close contact with someone who has meningitis is important.
Good hygiene: Washing hands regularly and covering the mouth when coughing or sneezing can help prevent the spread of meningitis.
Long-term management of meningitis
Long-term management of meningitis may involve ongoing treatment for any complications that occur as a result of the infection. Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is important for monitoring any long-term effects of the infection.
What is recent research saying about meningitis?
Recent research on meningitis includes:
A recent study found that some individuals may be more susceptible to meningitis due to genetic factors.
Researchers are also exploring new vaccination strategies to improve the effectiveness of meningitis vaccines.
A study published in 2020 found that individuals with COVID-19 may be at increased risk for developing meningitis.
Where can I go for more information on meningitis?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Mayo Clinic, and the Meningitis Research Foundation are helpful resources for information on meningitis. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider for guidance and support in preventing and managing meningitis.

