Small Cell Lung Cancer
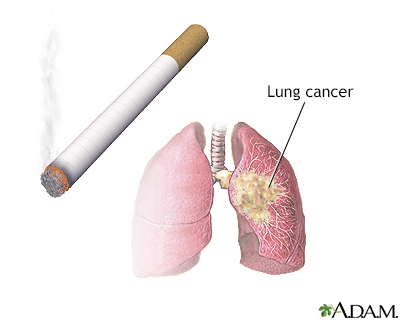
What is Small Cell Lung Cancer?
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) is a highly aggressive form of lung cancer that accounts for approximately 15-20% of all lung cancer cases. It is characterized by small cells that multiply rapidly and form large tumors which can spread throughout the body swiftly.
Who's at Risk for Small Cell Lung Cancer?
The primary risk factor for SCLC is smoking, with most cases appearing in current or former smokers. Secondary risk factors include exposure to radon gas, asbestos, and other occupational hazards. Family history of lung cancer and previous radiation therapy to the chest may also increase risk.
What Causes Small Cell Lung Cancer?
SCLC is primarily caused by smoking, with the harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke damaging lung cells over time. Other causes include exposure to harmful substances like asbestos or radon, and less frequently, genetic predisposition.
How Does Small Cell Lung Cancer Start?
SCLC begins in the respiratory cells located in the bronchi in the center of the chest. Over time, the cells mutate and grow uncontrollably, forming a mass or tumor. These cells can then spread to other parts of the body.
What are the Symptoms of Small Cell Lung Cancer?
Symptoms of SCLC can include coughing, chest pain, shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing up blood, loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue. In some cases, symptoms may not appear until the disease has advanced.
How is Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of SCLC often involves a series of tests, including imaging tests like X-rays or CT scans, sputum cytology, and a biopsy to examine tissue under a microscope. A complete blood count (CBC) and other blood tests may also be used.
How Can Small Cell Lung Cancer be Treated?
Treatment options for SCLC depend on the stage of the cancer and can include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, or a combination of these. Surgery is less commonly used due to the aggressive nature of this cancer.
What Complications May Occur with Small Cell Lung Cancer?
Complications from SCLC can include spread of the cancer to other parts of the body, such as the brain, liver, or bones. Additionally, paraneoplastic syndromes, which are rare disorders triggered by the body's immune response to the cancer, can occur.
How Can I Prevent Small Cell Lung Cancer?
The most effective way to prevent SCLC is to not smoke or to quit smoking. Regular medical check-ups can also help detect the condition early, and limiting exposure to carcinogenic substances can also reduce risk.
Long-term Management of Small Cell Lung Cancer
Long-term management of SCLC can involve ongoing treatment to slow the progression of the disease, managing symptoms, and regular follow-ups to monitor for recurrence. Psychological support and palliative care can also be crucial aspects of long-term care.
What is Recent Research Saying About Small Cell Lung Cancer?
Recent research on SCLC is exploring new treatment options, including targeted therapies and immunotherapies. Studies are also underway to better understand the genetic and molecular mechanisms of this aggressive cancer.
Where Can I Go For More Information on Small Cell Lung Cancer?
For more information on SCLC, you can visit websites such as the American Cancer Society, the National Cancer Institute, and the Lung Cancer Foundation of America.

